Get up to date with the latest HitGen articles and join us in the events
Protein-protein
interactions (PPI) are physical and chemical contacts between two or more
protein molecules. As a fundamental aspect of almost all biological processes, any
interference of the sophisticated PPI network could result in potential
physiological disorder or disease. Although some PPI networks have been well-established
for their roles in tumor development and therefore have been recognized as
potential oncological targets (Figure 1), PPI-based drug discovery is challenging
due to its possible event-driven conformational alteration and interface
accessibility variation. DNA-encoded Library (DEL) selection, an affinity-based
small molecule selection process, is considered a powerful PPI-based drug
discovery tool. With strong understanding of the target PPI mechanism of actions
(MOAs) and rational design of interaction partner group, DEL is capable of
providing selective hits with desirable MOA and potentially, designated
function.
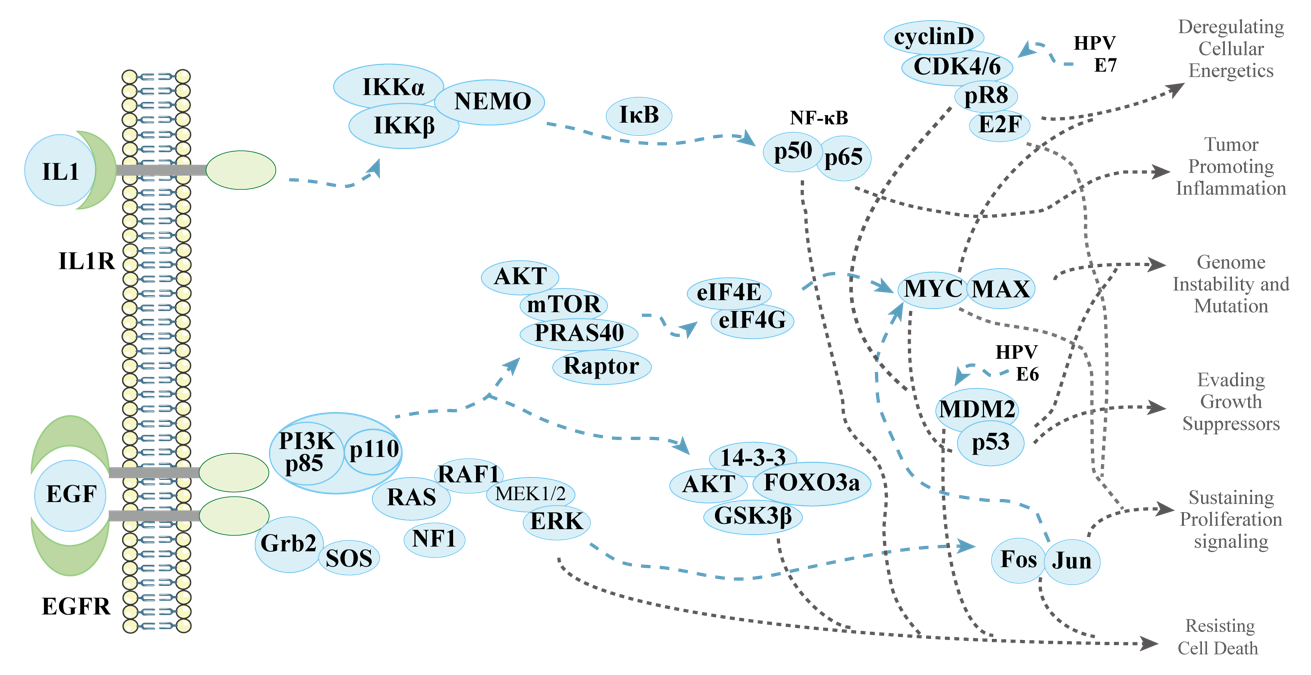
Figure 1, an example of PPI network in tumor development related processes.
Direct PPI blocker identification
One of the biggest
challenges for PPI disruptor identification is that the “coverage” of small
molecules might differ from that of the interacting motifs in PPI process. This
is largely due to the aforementioned intrinsic nature of PPI that the
interaction sites are more of a shallow and large interface rather than a deep and
well-defined pocket. With its great diversity, DEL has been providing PPI interface
binders for over a decade at HitGen, and a large portion of the identified binders
has been later confirmed as bona fide PPI blockers in the follow-up validation studies.
For example, aiming to target the interactions between the IL17A and IL17RA for
treatment of autoimmune and autoinflammatory diseases, HitGen has conducted a DEL
selection, and novel IL17A/IL17RA PPI interrupter have been identified and
compounds through medicinal chemistry optimization have now been nominated as preclinical
candidates.
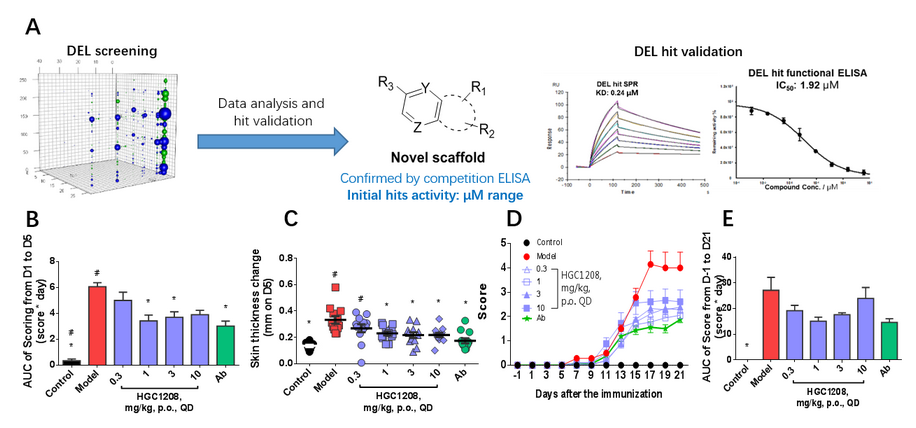
Figure 2, A) A successful hit series identified by DEL
for direct IL17A/IL17RA interaction disruption. DEL-derived compounds showed efficacy
in IMQ-Induced psoriasis model (B, C) and EAE model (D, E).
“Smart Selection Campaign”: function oriented hit
identification
PPI could be
modulated due to the conformational alterations of the interacting proteins
upon particular signaling event, such as ligand binding, co-factor interaction,
pH variation, and others. These PPI regulation processes could lead to pathway activations
upon complex formation, or switches to be turned on and off with domain
orientation change upon presence or absence of co-factors. At HitGen, “Smart
Selection Campaign” was developed to explore the binding capability alteration
and conformation-based regulation in PPI ligand discovery. By conducting DEL screening
in the absence or presence of partner proteins, co-factors, activators and/or
inhibitors, this hit identification process has already provided vast amount of
information of potential function of the candidate.
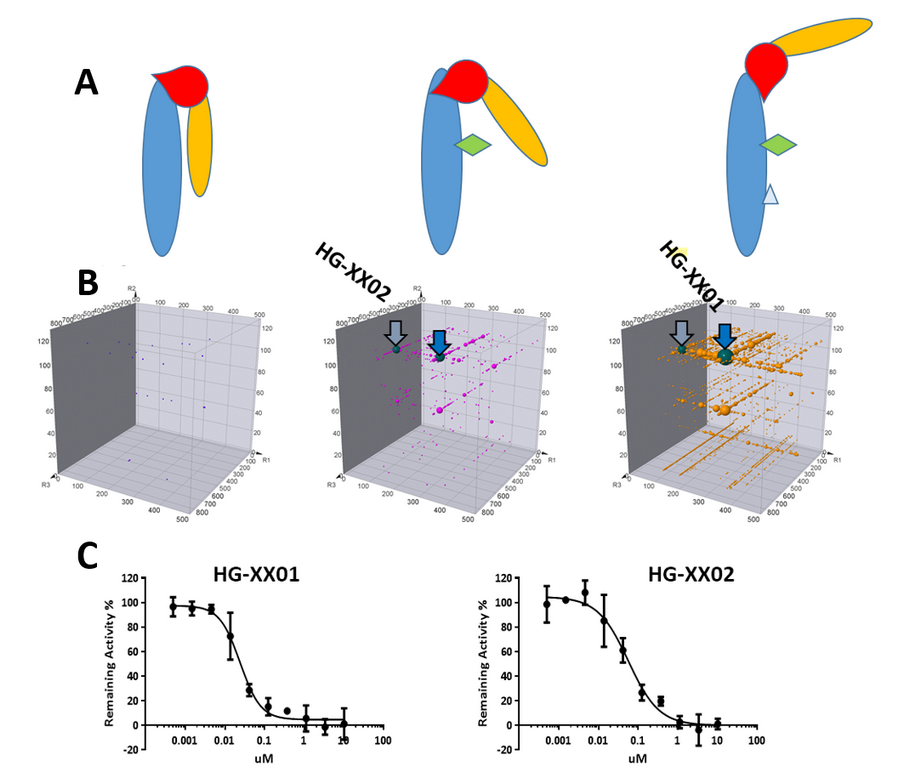
Figure 3, A) Conformation change upon presence of
different cofactors for a PPI target introduces different binding capabilities.
B) Different series of compounds identified from DEL selection with
conformational specificity. C) Confirmed hits from different series.
Identification of specific binder with Special MOA
In a particular DEL
selection conducted at HitGen, the PPI network for the target of interest was complicated
because different pathways are activated upon binding to different co-factors.
On the one hand, target protein could form a heterodimer with partner protein 1 and further form a ternary
complex with protein 2 to initiate
the downstream signaling pathway. On the other hand, the same target protein
could form a different heterodimer with partner protein 3, leading to a bypass pathway. By including all the
partner proteins in our DEL selection with different combinations to reflect
all possible scenarios, several hit series were identified, and one of the
series could specifically bind to the target-protein
1 complex. In the subsequent hit validation studies, we also found that
this binder series could stabilize the target-protien1 complex and more
importantly, this stabilization prevents the formation of either the ternary complex, or the target-protein 3 complex. Therefore, we
have identified a specific PPI stabilizer series with dual functions at once.
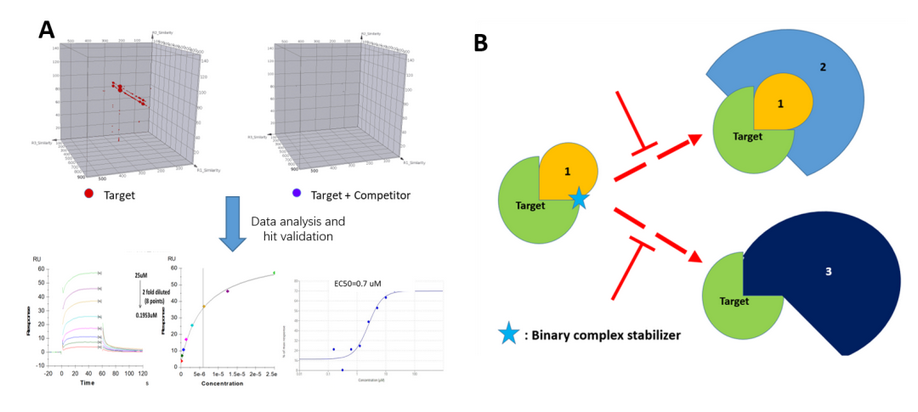
Figure 4, A) a series of hits identified by DEL and
confirmed with orthogonal methods. B) Further MOA study demonstrated that in
the presence of the confirmed hit compound, two PPI cascades have been
interfered based on a special MOA.
DEL
for PPI at HitGen
With profound understanding of the PPI target MOA and
highly case-dependent DEL selection plan, all possible conformational
alterations and different interactions with different partners will be included
in our selection to simulate the actual PPI processes and maximize the chance
of identifying robust hits with good affinities and properties. HitGen’s “Smart Selection Campaign” (Figure 5) along
with our trillion size DEL, have enabled
PPI-targeted drug discovery with easier design and more straightforward execution.
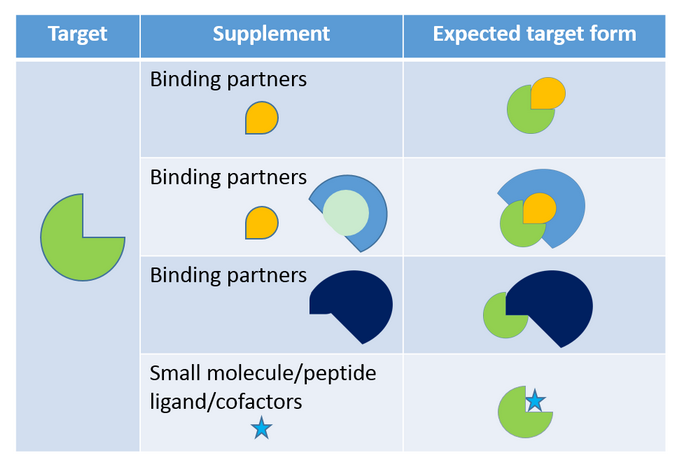
Figure 5, An example of possible selection groups
to explore all possible target forms in one selection campaign
We use cookies to provide a better web experience.
By using our site, you acknowledge our use of cookies and please read our Cookie Notice for
More information